Understanding Thoracic Four Syndrome: New Insights into Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment
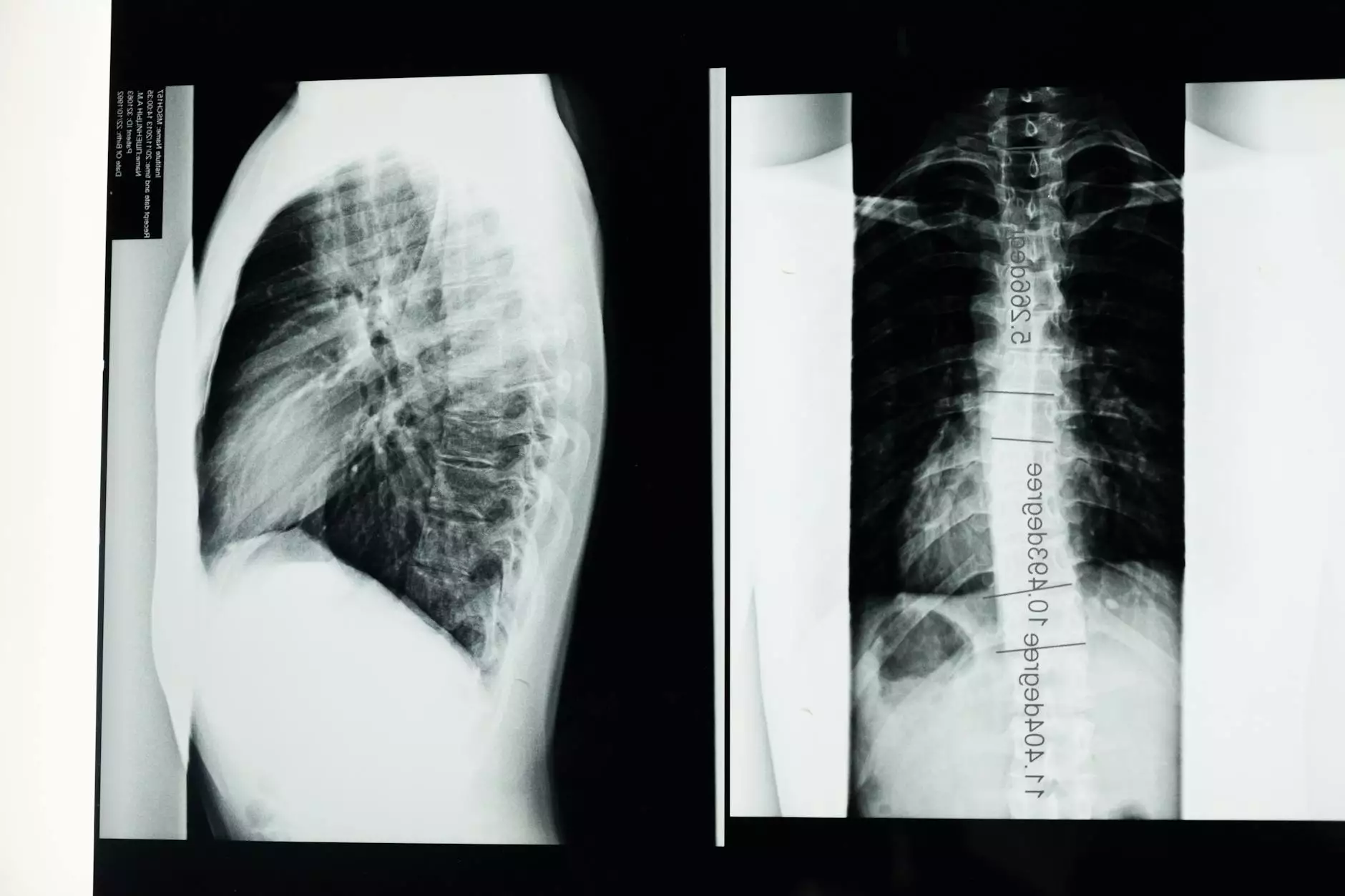
In the realm of health and medical advancements, few topics garner as much attention as conditions affecting the thoracic region of the spine. One such condition is known as Thoracic Four Syndrome. This article delves deeply into the intricacies of this syndrome, offering comprehensive insights into its pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment options.
What is Thoracic Four Syndrome?
Thoracic Four Syndrome primarily affects the fourth thoracic vertebra (T4) and its associated structures. It is characterized by a range of symptoms that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Understanding T4 syndrome involves an exploration of how the spine interacts with the nervous system and the musculoskeletal system.
Symptoms and Clinical Features
Individuals suffering from Thoracic Four Syndrome often experience a variety of symptoms, which may include:
- Localized pain in the upper back region.
- Radiating pain towards the shoulders or arms.
- Numbness or tingling sensations.
- Muscle weakness in the arms.
- Postural changes leading to increased discomfort.
These symptoms can vary widely among individuals, often leading to misdiagnosis or delayed treatment.
Pathophysiology of Thoracic Four Syndrome
Delving into the pathophysiology of Thoracic Four Syndrome reveals the underlying mechanisms that contribute to its development. The fourth thoracic vertebra plays a crucial role in the spine's stability and function.
Neurological Implications
The thoracic region houses spinal nerves that are pivotal for upper body function. Compression or irritation at the T4 level can lead to neural dysfunction, resulting in symptoms such as pain, weakness, and autonomic dysregulation. Conditions such as herniated discs or spinal stenosis in this region can exacerbate symptoms significantly.
Biomechanical Factors
Biomechanical factors associated with Thoracic Four Syndrome may include:
- Poor posture: Prolonged periods of poor posture can stress the thoracic spine.
- Repetitive strain injuries: Activities that involve repetitive movements can lead to cumulative trauma.
- Muscle imbalances: Weakness or tightness in adjacent muscle groups may contribute to pain and dysfunction.
Diagnosis of Thoracic Four Syndrome
Diagnosis of Thoracic Four Syndrome often involves a multifaceted approach. Understanding the clinical features and pathophysiology aids healthcare professionals in determining the correct diagnosis.
Clinical Assessment
The initial assessment typically includes a thorough patient history and physical examination. During the examination, a clinician may:
- Assess the range of motion in the thoracic and cervical regions.
- Perform neurological examinations to evaluate function in the upper extremities.
- Conduct palpation to identify areas of tenderness or muscle tightness.
Imaging Techniques
Imaging studies play a vital role in confirming the diagnosis of Thoracic Four Syndrome. Common imaging modalities include:
- X-rays: Useful for identifying structural abnormalities.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Provides detailed images of soft tissue structures, including intervertebral discs and spinal nerves.
- Computed Tomography (CT) scans: Offers comprehensive images of bone structures and can reveal complex anatomy.
Treatment Options for Thoracic Four Syndrome
Treatment for Thoracic Four Syndrome is aimed at alleviating symptoms, improving spinal function, and enhancing quality of life. A multidisciplinary approach often yields the best results.
Conservative Management
Initial treatment typically involves conservative management, which may include:
- Physical therapy: Tailored exercises can strengthen supportive muscles and improve flexibility.
- Chiropractic treatment: Manipulative therapy can help restore spinal alignment and relieve pressure on nerves.
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can ease pain and reduce inflammation.
Interventional Approaches
If conservative measures prove ineffective, interventional options may be considered, including:
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections can offer temporary relief from inflammation and pain.
- Surgery: In cases where structural issues are significant, surgical intervention such as decompression may be necessary.
Education and Awareness
Raising awareness about Thoracic Four Syndrome is essential for early diagnosis and effective management. Education for both healthcare providers and patients about the symptoms and potential treatment pathways can lead to improved outcomes.
Future Directions in Research
Current research into Thoracic Four Syndrome focuses on identifying new treatment modalities and understanding the long-term effects of the condition. Areas of interest include:
- Biomechanical studies: To explore how different postural habits influence the development of T4 syndrome.
- Longitudinal studies: To assess treatment efficacy over time and identify the best practices in management.
- Patient-centered research: To gain insights into patient experiences and improve care strategies.
Conclusion
In summary, Thoracic Four Syndrome is a complex condition affecting many individuals. Understanding its pathophysiology, recognizing its symptoms, and ensuring appropriate diagnosis and treatment are vital for improving patient health outcomes. As a field, health and medical education continues to evolve, staying informed about such conditions will promote better prevention strategies and therapeutic options. By continuing to investigate the intricacies of conditions like Thoracic Four Syndrome, we set the stage for better healthcare practices and improved patient care.
For more detailed insights, visit the case report at IAOM US.
https://iaom-us.com/thoracic-four-syndrome-case-report-new-insights-pathophysiology-diagnosis-treatment/








